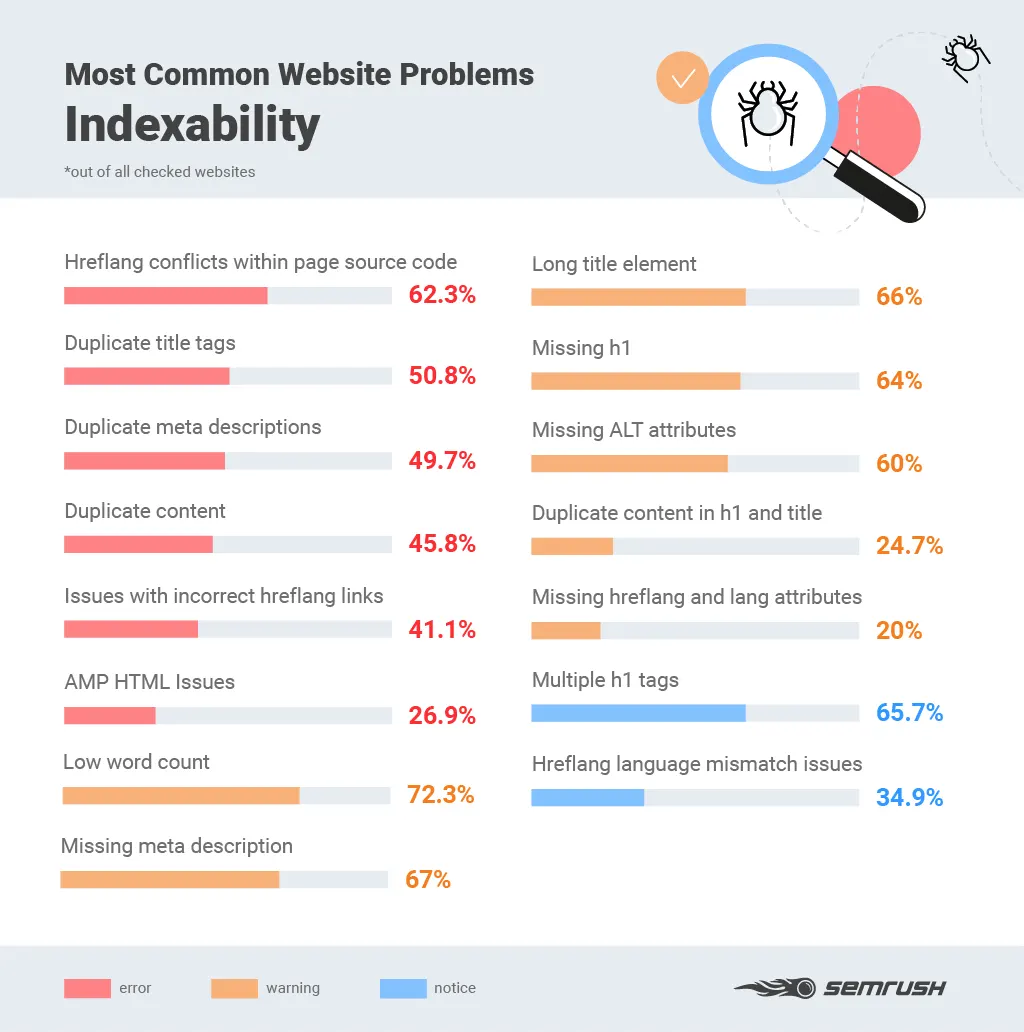
For colleges and universities, optimizing a website for search engines has become an enrollment imperative. Higher education institutions need to rely increasingly on search engine optimization (SEO) to drive website traffic, where they can then convert visitors into prospective students, donors, and advocates.
A whopping 93% of online experiences begin with a search engine such as Google, Yahoo, or Bing. Forbes
Table of Contents
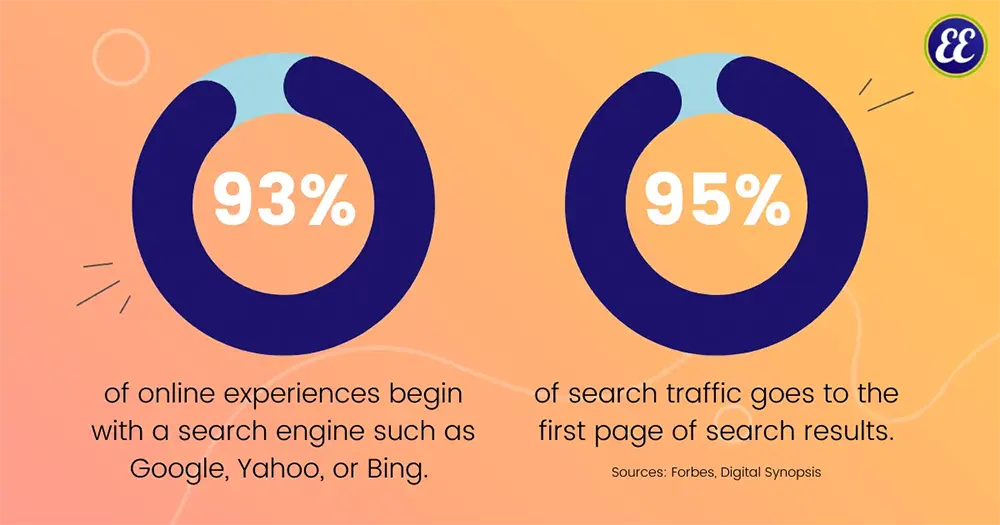
95% of search traffic goes to the first page of search results Digital Synopsis
Your university already has a website. As a first step, to increasing your organic traffic (without spending money on paid media), is to do an SEO (search engine optimization) audit.
Google uses more than 200 ranking factors for its search algorithm (source)
This type of audit is essential in identifying weaknesses, recognizing untapped opportunities to grow enrollment, and improving the quantity and quality of traffic coming to your website.
An SEO audit allows you to discover and fix issues that could be negatively affecting your website’s search engine rankings. The better shape 💪your website is in, the more likely it will rank higher in search engines and drive more traffic to your website.
And, each year, companies and universities spend more than $79 billion on search engine optimization (SEO).
Consider conducting an audit regularly – there’s always room for improvement!
This article will break down the necessary steps to audit your website and increase your chances of being ranked higher by search engines, to drive more awareness for your programs and more enrollments.
Why Your University Should Invest in SEO
SEO encompasses several techniques to help improve the chances your Higher Ed website will appear on the first few pages of search engines like Google. While everyone’s goal is to become the #1 result on Google for terms like “bachelor’s degree”, “online degree”, and other similar phrases, it’s impossible for every institution to rank #1 for the most competitive search terms.
Dictionary.com defines SEO as “the methods used to boost the ranking or frequency of a website in results returned by a search engine, in an effort to maximize user traffic to the site.”
90% of pages receive zero organic traffic (source)
SEO is driven by the right keywords that prospective students would use to find your school or programs. Optimizing your website improves your chances of being found for those targeted phrases.
Search engines are the predominant source of website traffic, so incorporating these phrases or keywords into your copywriting is essential, but it’s only one piece of the pie.
SEO can potentially save your university money in the long run. – rather than paying for Google ads and display ads, a well-optimized website can increase your school’s enrollment success year after year.
Getting to page one of the search results is vital.
- 75% of users don’t even click past the first page!
- The first three organic search results get 60% of all traffic from a web search.
- Leads coming from a search have a 14.6% close rate, compared to just 1.7% from channels like print or direct mail advertising.
- 95% of new pages do not reach the first page of search results for the first year (Source)
What Is an SEO Audit?
An SEO audit is a review of your entire website to assess how well you are ranking and what next steps you can take to improve visibility and organic traffic. The term “organic” in SEO simply means a potential student finds you on a search engine without clicking on an ad.











How to Audit Your Higher Ed SEO Website
Auditing your website requires a series of steps that will help you identify areas of improvement. Our SEO experts have identified 11 key steps to a successful audit. Read on to learn about each step in more detail:
- Setting up the SEO basics
- Technical audit: Run a thorough deep crawl of your website to identify possible technical issues
- Keyword Research: How to best identify the right keywords to target and how to incorporate them into your content
- Metadata: Check and adjust your metadata to be keyword rich
- On-page audit: Perform a content audit and gap analysis of your content to ensure you are creating valuable content and meeting searcher intent
- Off-page audit: Audit your external linking versus your competitors
- Content repurposing
- Run a competitor analysis of your website against a set of competitors
- Optimize video SEO
- Confirm your website is mobile-first
- Measure the impact

Step 1: SEO Basics
Before tackling the tough stuff, we need to make sure we have the basics taken care of first. If you don’t have these programs, plugins, and actions taken care of already, take the time to do so (and soon).
Your SEO checklist should include:
- Setting up Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster tools
- Setting up Google Analytics
- Installing and configuring an SEO plugin (for WordPress or other platforms)
- Generating and submitting your sitemap to Google Search Console and Bing Web Developer tools
- Creating a Robots.txt file
- Checking Search Console for manual actions and running a variety of reports
Step 2: Technical SEO: Run a Deep Crawl Analysis of Your Website
Once you have your foundation ready, it’s time to move on to the technical SEO analysis. This step will help your team better understand if there are hurdles standing in the way of improving your search engine visibility. Think of a technical SEO analysis as checking your home’s foundation before building on an addition. There are many tools available to help ensure your foundation is solid and ready for what comes next.
Technical research tools we recommend:
- Google Search Console
- Google Analytics
- PageSpeed Insights
- Merkle Schema Markup Generator
- Semrush Site Audit
- Structured data markup helper
- Google’s mobile-first test
You can run a deep crawl of your website using tools like Screaming Frog, Semrush, Ahrefs, Sitebulb or Deep Crawl.
What to focus on when running an SEO technical analysis:
- Page security: This is the padlock symbol to the left of the URL. It not only influences a user’s perception of a non-secure website, but Google is actively punishing non-secure websites by lowering their rankings.
- Page loading speed: This is the loading speed of your pages when someone clicks on your website link from search engines or paid ads. Website site speed is a significant factor in how Google ranks your content. Research shows that every additional second it takes your website to load can cost up to 7% of its conversions. (source)
- Crawlability: Improving crawlability helps Google search only the relevant pages of your website. Not every page or section of your website needs to be crawled and indexed.
- Website errors: For your technical audit, you will want to identify and remove all broken links, which will show up as 404 pages. You can go into Google Search Console and use the Error Report functionality to help you identify these issues.
Technical SEO checklist:
- Leverage the “inspect URL” feature in Google Search Console
- Ensure your website is mobile-friendly (better yet, mobile-first)
- Check your website’s loading speed
- Make sure you are HTTPS instead of HTTP
- Find and fix crawl errors
- Check your website page depth and make sure your more important pages fall within a three-page depth as a best practice
- Check for duplicate versions of your website
- Identify and fix broken links
- Use an SEO-friendly URL structure
- Fix orphaned pages
- Check canonical tags
- Add structure data


Get a Complimentary SEO Audit to unlock hidden pockets of growth and cost savings
Schedule a brief discovery call to receive a complimentary consultation for your business.
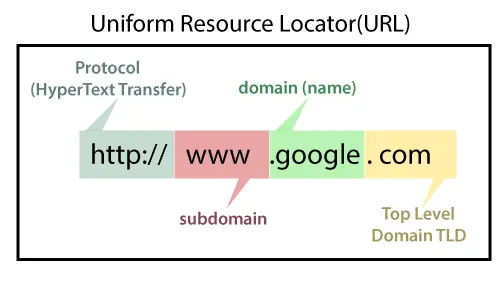
URL structure
Is your website organized by modality and by your programs or colleges? If not, it’s time to reevaluate your URL structure.
Below are examples of good vs. poor URL structure:
Good URL structure:
https://example.com/category/service
Poor URL structure: https://example.com/year/month/category/subcategory/subcategory/tag/keyword-keyword
Subdomains and URL best practices
- Make sure your domain name is easy to say, remember and type
- Include a keyword in your domain name while keeping it brand-friendly
- Do not use hyphens in your domain name as it is not memorable
- Use subfolders instead of subdomains, so Google can crawl your site easier
Moz.com explains what roadblocks can come from domain issues and how they impact SEO performance.
It’s essential not to change your domain name as it signals to Google that you are a new site. This may lead you to lose “points” in the algorithm. However, sometimes brand names change, and the URL name needs to change. If that happens, expect a large drop in traffic for 9-18 months after your URL change. It certainly doesn’t mean you can’t rank on Google’s first pages, but it will delay your plan as Google catches up.
Step 3: Keyword Research
How to identify the right keywords to target and incorporate them into your content:
Hubspot defines keyword research as:
“The process of finding and analyzing search terms that people enter into search engines with the goal of using that data for a specific purpose, often for search engine optimization (SEO) or general marketing. Keyword research can uncover queries to target, the popularity of these queries, their ranking difficulty, and more.”
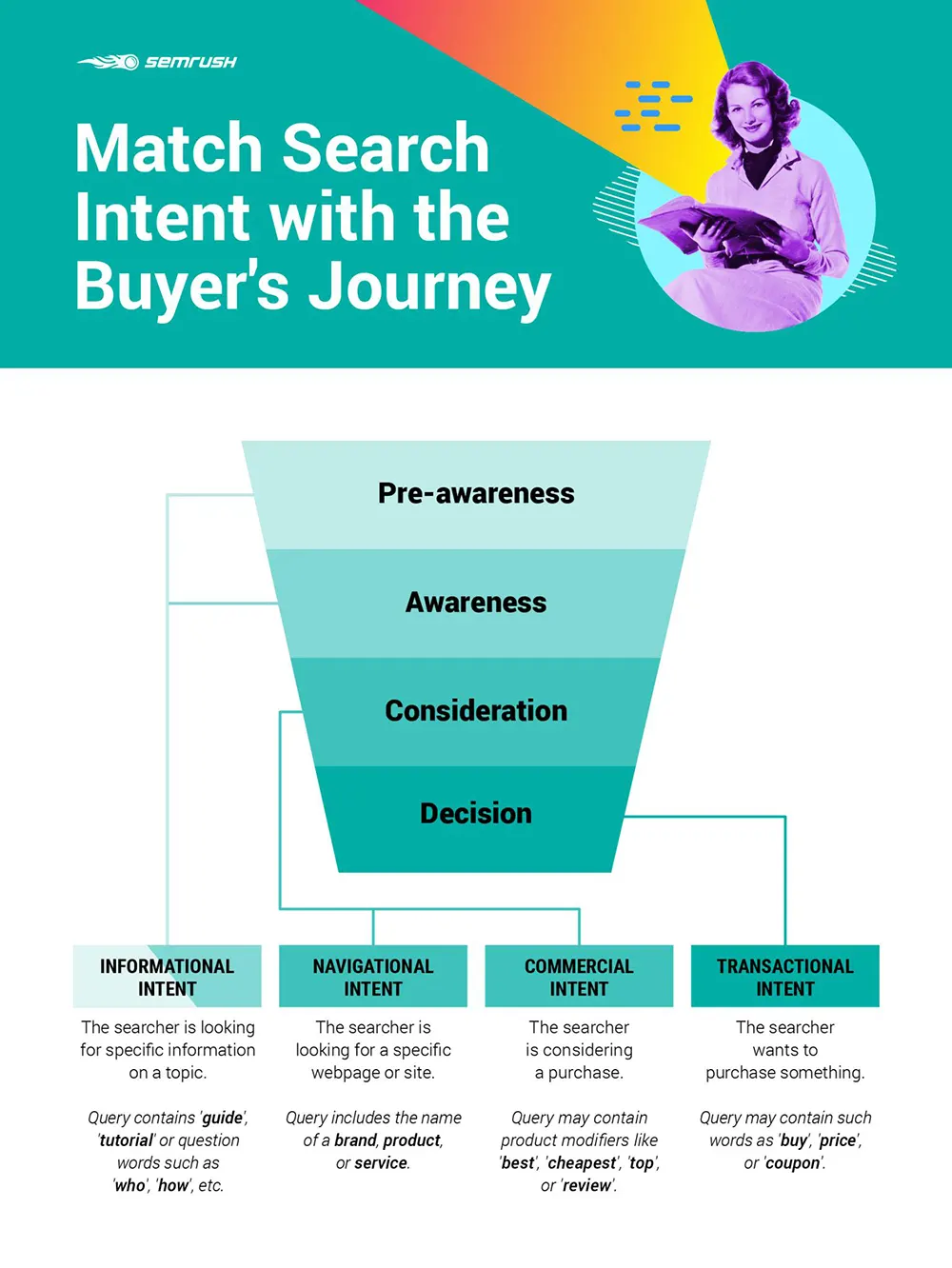
Focus on the semantics
Understanding semantic search will help you understand what your prospective students are really looking for. What people type into a Google search nowadays is much more conversational than it’s ever been before.
More recently, search engines (primarily Google) have evolved to understand the intent and context – or semantics – behind every user search.
This creates an obvious need to analyze and understand search intent before creating content. For example, let’s say someone searched “the ring of all rings”.
Instead of displaying different types of rings one can buy for their wedding day or special occasion, Google knows the user is referring to Lord Of The Rings – despite not including any book titles in the search.

The first page of search results is then packed with information on different rings within this specific story – all because it assumes the intent and context of the search was related to Lord Of The Rings.
It all comes down to proactively adhering to your prospective student’s conversational tone. The ideal tone for your website copy should mimic a conversational tone versus an academic one.
Try practicing a semantic search and answer questions appropriately. There’s a lot of friction in the student’s journey, and the easier you make it for someone to decide that your university and program are right for them, it is all more likely they will apply to enroll.
It’s important to understand the intent behind the keyword search.
For example, someone Googling “Orlando aquarium near me” is likely looking for an attraction that showcases ocean life and not looking to buy a saltwater aquarium. On the other hand, if your business focuses on selling saltwater aquariums, fish, and supplies, people looking for ocean-related theme parks aren’t likely to convert into buyers.
Our team worked with a Higher Ed client who was proud some of their blogs were receiving over 5,000 visitors but perplexed why these visitors were not converting into inquiries. These blogs were catered to people looking to understand MLA formatting. Who needs to do MLA formatting? Probably someone who is already in college – so their intent to find a college and enroll is very low.
Be sure to pick keywords that have higher intent to become prospective students. Another reason to optimize for keyword intent is it will help to drive your content strategy.
Keyword research will be required to help you create a search engine-friendly website.
Keyword research is not difficult, but it can be tedious. Below are some tools and steps to get you started.
Keyword research tools:
- Semrush Keyword Magic tool
- Semrush Keyword Gap tool
- Ahrefs keyword explorer
- Google Ads Keyword Planner
- Semrush Topic Research
- Keywords Everywhere
- People Also Ask
- Answer the Public
- iSpionage
How to Start Higher Ed Keyword Research:
- Start by identifying five to ten different degree programs or locations where you are located, including your state and local cities, and match these with modifiers such as college, university, school, or degree. Here’s an example of how you will use these location modifiers using North Carolina: North Carolina college, North Carolina university, North Carolina school, North Carolina degree.
- Analyze your keywords based on their intentions.
- Research these terms and phrases by using the tools mentioned above.
- Identify your competitors.
- Conduct a keyword gap analysis.
- Find question keywords. Identify what people are asking about on the internet and answer these questions in your content.
- Create a keyword map.
- Analyze the intent of pages that currently rank well.
- Prioritize by search volume and keyword difficulty. Leverage the Google Keyword Tool to determine keyword search volume. The intent of the keywords is more important than the volume, but ideally, try to target keywords above 100 monthly searches. However, some sites are seeing great results from targeting zero search keyword phrases.
- Finally, complete a content audit to see if you already have keywords targeting the new keywords you’ve discovered. If there are no pages on your website targeting those keywords, then add it to a list of new content to create. First, choose the main keyword or phrase for each content page, then add that and a few secondary keyword terms to your copy (use the main keyword eight times, including in the title).
If prospective students search the web to answer specific questions such as “what career can I have in criminal justice?” or “what degree can I earn in North Carolina?”, then consider creating content to answer these questions or provide value back to prospective students.
The keyword research tools mentioned above will help you figure out what your prospective students are searching for. Picking relevant keywords will also help you seem more authoritative to Google.
By taking the time to start with this step, you will be well on your way to improving your visibility in search engines to prospective students who are most likely to enroll.
There are also best practices for writing website copy for search engines and users. Consider hiring an SEO copywriter to help you create the best pieces of content for your website.
Step 4: Check Your Meta Tags

Get a Complimentary SEO Audit to unlock hidden pockets of growth and cost savings
Schedule a brief discovery call to receive a complimentary consultation for your business.
But first…what are meta tags?
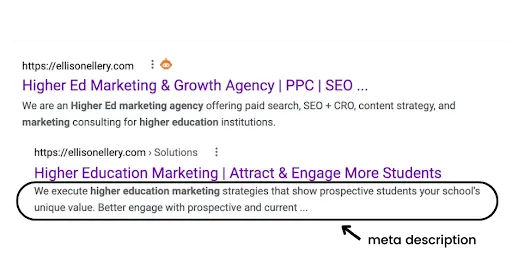
Meta tags are a type of HTML tag that provide search engines with information about a website page. While metadata isn’t as important for SEO rankings as it used to be, the meta description still plays a role in on-page SEO. Plus, your title tag and meta description can help to attract a prospective student to click on your website.
A meta description is an attribute within your meta tags that help describe your page. This snippet of text may appear in search engine results under your headline. If your meta description is not optimized, search engines will pull a snippet of text from the main body copy of the page instead.
Each one of your website pages will need your meta tags filled out and optimized.
Here is an example from our website:
Metadata to review on your website:
- Title tag
- Meta description
- Canonical tag
- Alternative text (Alt) tag
- Robots meta tag
- Social media meta tags (open graph and Twitter cards)
- Responsive design meta tag
Here are five tips to help you optimize your meta tags for Higher Ed SEO:
- Title tags should be clear, descriptive, and contain no more than 60 characters. They will appear in search results, titles, and anchor text for social sharing.
- The meta description should accurately describe what your page is about. It’s the snippet displayed below your title on search engines and social shares.
- Similar to the file robots.txt, the robot meta tag tells Google what pages to index. It is crucial to remove pages that do not need to be indexed.
- Write alt tags for your visual assets using keywords to maximize search engine relevance rankings.
- Use the Header tag (h1, h2, h3, etc.) for cueing search engines on the subject of your page.
Step 5: On-Page Audit
Performing an audit and gap analysis of your content will help ensure you are delivering value and meeting searcher intent.
With a strong content strategy in place, you can strategically attract your ideal audience and watch them grow from strangers into enrolled students. Learn how to do a content gap analysis for SEO.
Whether it’s a landing page, one-pager, or social media content, focus on the benefits and key differentiators of your degree or university to help your buyers understand why you should be their top choice.
Once you have completed your content gap analysis, it’s time to look at creating a solid content strategy that includes repurposing the content you create.
Read this guide on how to create a content marketing strategy that will engage your prospective students.
You will not need to audit or refresh all of your website content pages. Focus on the ones already ranking well for certain keyword phrases or focus on improving those high-quality pages by updating their content and linking other pages to these higher-quality pages.
Content gap analysis (competitor research)
Review the content your competitors rank for and identify the gaps where your competitors show up for keywords and your university does not. This will help you prioritize which keywords and topics to pursue moving forward. The complete guide to how to do a content gap analysis.
Finding hidden text
Search engines and visitors will see your website content differently depending on CSS styles or JavaScript. Even on our website, we figured out extra code was coming over when we would copy and paste from Google docs. Our Web Developer was having to go into each page and strip it from this extra code. This happens with Microsoft Word docs too.
It’s important to look at your page through the eyes of Googlebot, which will allow you to check for hidden text. Can you see whether your intended text is showing up, or is it hidden by JavaScript? You can download this web developer tool browser add-on to make this process easier.
Writing content for prospective students and search engines
According to HubSpot, 43% of people skim blog posts instead of reading the entire content.
Establishing the best structure for your Higher Ed SEO content with a consistent format will make it easier for readers to stay engaged and learn from your institution – leaning into your brand more and more.
Here are a few suggestions when it comes to formatting SEO content, especially longer-form blog posts, articles, and landing pages:
- Be distinct on your headings and subheadings: Use H1 and H2 tags that include your focus keyword and commonly asked questions about the topic
- Keep each paragraph to just a few sentences
- Bold or italicize important points
Optimize with a call to action
If you are sending paid media traffic to any of your pages, be sure to follow these Higher Ed landing page best practices.
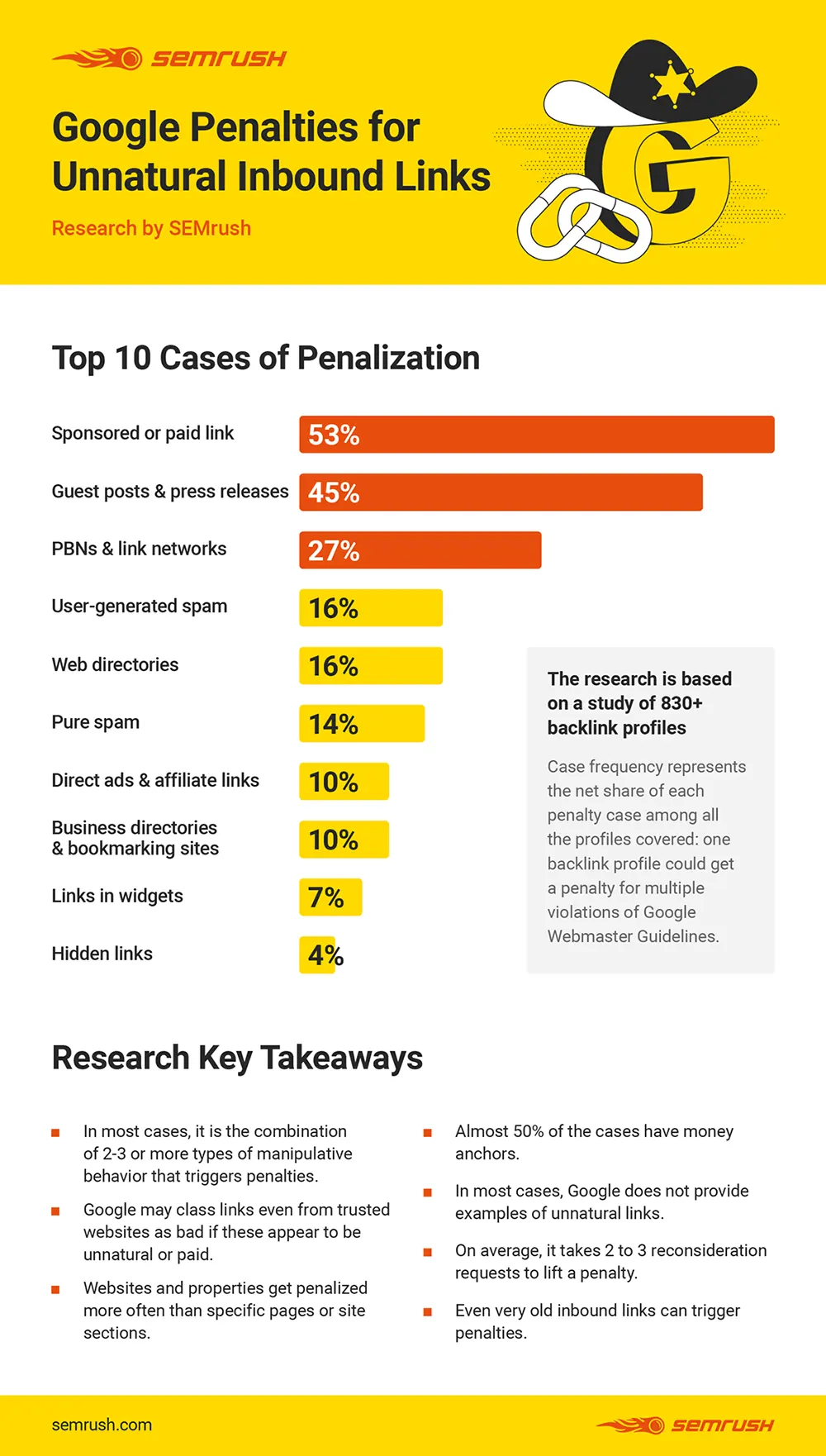
Step 6: Off-Page Audit: Link Building
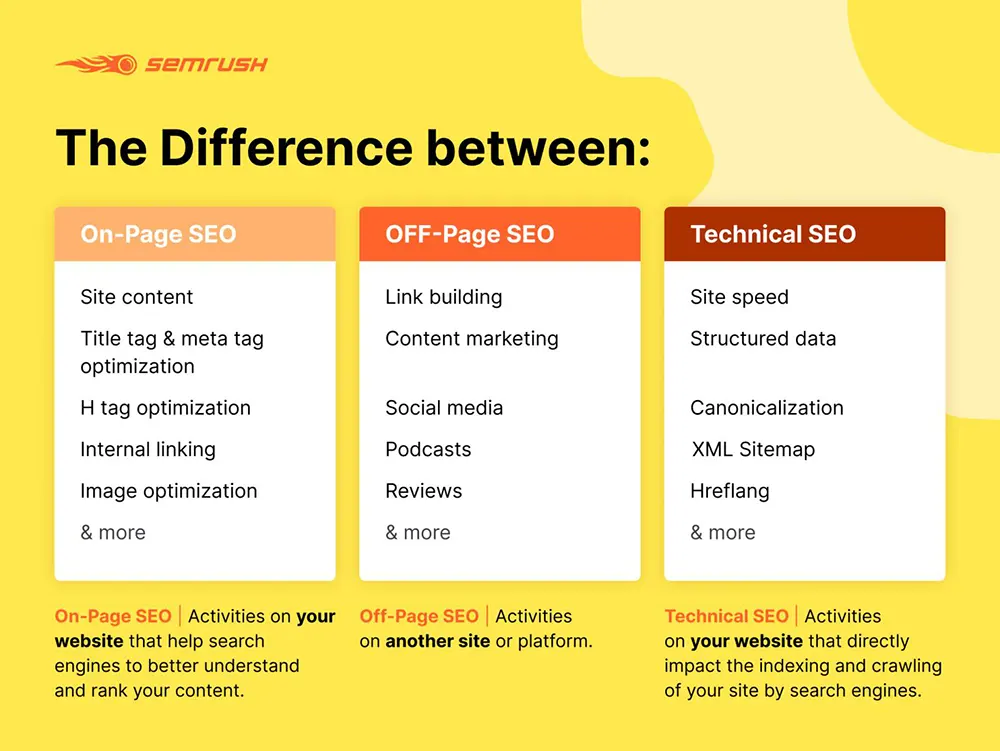
The most important aspect of off-page SEO is link building.
To build long-term organic search success, you need to show your target audience your brand is authentic, relevant, and consistently offers quality information.
When other businesses believe this to be true and link back to your pages, it creates a ripple effect of increased traffic and search results.
Off-page optimization is the process of improving your search engine rankings by making adjustments outside of the website, primarily through link building. Google counts the number and quality of links to a page (PageRank) to determine the importance of a website.
The analogy the industry has been using for years is to think of links as votes in a political election. Generally, in local elections, the candidate with the most votes will win. This is also true for link building – expect the quality of your links matter more than how many you have. If you get a link from a reputable website, it can be more valuable than getting 100 links from poor-quality websites that rank poorly.
Getting traffic to your website from Google and other search engines can be difficult, especially if you don’t already have many links pointing to your website or you’re trying to get your website to rank in competitive niches.
Other websites linking to your pages tell Google your brand is worthy of citation, earning your website higher rankings in search results. Acquiring hyperlinks from other websites to your own (that you didn’t ask for) is like reaching the peak of Mt. Everest for SEO.
So how do you climb the treacherous mountain of link building? Here are a few suggestions on how to reach success:
- Submit guest blog posts to websites in your industry. Your audience is most likely visiting the website anyway, so why not make yourself known? Keep in mind that your goal is not only to get a higher search ranking but also provides your audience with quality content. Google algorithm will identify the low-quality links, and your website may be penalized.
- Social media marketing. Reviews, mentions, and getting your brand name out there to influencers in your industry will help demonstrate your knowledge and authority. The power of social media is not something to underestimate!
- Email outreach. Reach out to journalists, bloggers, and influencers directly with a well-written email and ask them to link to your pages. Remember to tell them why they should listen to your brand and what’s in it for them! Personalization has a habit of paying off eventually. Know that it may take hundreds of outreach emails to get a few links back
- Create sharable content. Learn more about how your university can create new content to pull people into your enrollment funnel. If you’re not generating excitement around your own brand with quality content, how can you expect others to do the same for you?

Get a Complimentary SEO Audit to unlock hidden pockets of growth and cost savings
Schedule a brief discovery call to receive a complimentary consultation for your business.
Both on-page and off-page optimization help determine the success of your SEO campaign. If you’ve accomplished one but not the other, you may not rank for the type of searches you’d hoped for, or you may not rank as high in search.
Additional resources and tracking success
Check out this blog post from HubSpot on how to garner more external links. When you learn how to garner external links more effectively, your rankings are more likely to increase, improving the likelihood you’ll drive more quality traffic to your website.
Here’s a recap of suggestions and other actions you can take to start driving a successful link building strategy (This list is according to Ahrefs):
- Link outreach
- Guest blogging
- Broken link building
- Unlink mentions
- Link reclamation
- Paid promotion for “linkable assets”
- Steal links from inferior pages
- Content repurposing & syndication
- Community site link building
Over time, you should track your website’s performance to see how well your external linking strategy is working. Look at traffic sources, volume, and rank positioning for your tracked search terms. If you see a significant increase in any of these metrics, your external linking is likely driving that bump in traffic to your site.
Overall, link building is a complicated topic. Here is an excellent guide on link building from Ahrefs and a free course on YouTube from Ahrefs on link building.
Step 7: Repurpose Content
What does it mean to repurpose content? Simply put, it is taking one piece of content like a long-form article and creating additional messages for complimentary mediums like videos, social media posts, infographics, shorter articles, and quote graphics.
The purpose of going through this exercise is not only to maximize your time but also to increase the reach of your article so that Google finds it more valuable. By pulling bits and pieces of a long-form article and putting them on other channels, you get extra “points” from Google. It helps in terms of credibility and consistency, which search engines value.
Backlinko, which we believe is a great resource, defines repurposing content as:
“Repurposing content (also known as “content recycling”) is the practice of reusing all or elements of existing content in order to expand that content’s reach.”
His definition can help us understand an important aspect of repurposing content – that it enables you to reach a broader audience while minimizing your content development to a manageable practice.
You should consider a long-form (1,000-3,000 words) blog post as your foundation.
Newsletter Sign up!
Get our best content on digital marketing in your inbox 2 times a month

You want to show off your brand and university’s values, but you need great content that is compliant to get there.
Learn more about creating an effective comparison SEO strategy from Semrush, and how to craft a competitive comparison landing page from Crayon.
Step 8: Competitor Research
Who are your competitors? Part of understanding your prospective student is knowing where else they might be looking to learn more about a career or a degree. Will they be searching a well-known competitor first? Creating and sharing comparison content with prospects can help prospective students decide which college is right for them.
When it comes to SEO, ask yourself, “what would our ideal prospective student be searching for right now if they wanted to compare us with XYZ university?”.
If you’re unsure, our agency can perform qualitative research for your university. Contact us here to schedule a discovery call.
Step 9: Video SEO
Yes, even your video content needs to be optimized! Video SEO is considered a mature marketing strategy for Higher Ed institutions. According to WordStream, 59% of senior executives will choose to watch a video over reading text if both are available. That number is so much higher for GenZ!!
In fact, Cisco has predicted videos will account for 82% of all web traffic by 2022.
Videos are undoubtedly boosting ROI. Most marketing and sales professionals have used video marketing in one way or another, and according to LinkedIn research, 73% of marketers say video positively impacts marketing ROI.
Why? It’s easy-to-consume content and more engaging for most prospects, making it necessary for any marketer to include in their SEO roadmap.
YouTube is the leading go-to video resource. Did you know driving traffic to your website from YouTube also boosts your Google search ranking? With YouTube being the most popular video site on the web, it’s also a premier search engine. When your company ranks higher on YouTube, it brings in more leads and makes that high-energy content production worth it in the end.
Your video title and description matter. Optimize both the title and description with well-researched keywords and phrases so your content is found and viewed. Keeping your video title to 70 characters or less and your description to at least 200 characters will help the platform understand enough about your content to help you rank in the right places. Don’t forget to also leverage tags, thumbnail images, and even optimize file names! Every word counts when it comes to Higher Ed SEO.

You can get you video transcription and add this to YouTube.
Developing video content take time, resources, creativity, and planning. With zero optimization strategy, you’re letting all that hard work go to waste. Your company has something to say – make sure it’s heard (by the right people)!
Step 10: Mobile-First
Google has been working on mobile-first indexing for quite some time. It was originally developed in response to the drastic shift in how people search (and browse) the web and the widespread adoption of mobile devices.
By March 2021, Google will have switched all websites from desktop-first to mobile-first indexing, having been through a transitional period of moving sites over when their systems recognized that they were ready to do so.
Any new websites launched after July 2019 automatically went to mobile-first indexing, but some existing sites have yet to be moved over.
It is safe to say that we now live and work in a truly mobile-first world.
Ready to learn more? Check out this resource: Mobile-First Indexing Explained: What You Need To Know from Semrush.
Step 11: How to Measure the Impact of Higher Ed SEO
Bringing in specialists to help track metrics can be the difference between owning a site that is building authority and trust versus getting lost in the Google black hole.
Many tools like Semrush, Ahfrefs and HubSpot offer reporting capabilities that allow you and other members in your organization to measure and strategize on specific numbers and results. If you don’t track your impact or partner with an agency to do the tracking for you, you may not know where you can improve processes to drive more enrollment.
Here are the main metrics your institution should track to ensure your SEO strategy is on the right path. Remember, slow and steady wins the marketing race:
- Organic traffic
- Keyword ranking
- Conversion rate
- Bounce rate
- Page load time
- Backlinks
- Mobile traffic vs desktop
- Brand keywords vs non-brand keywords
Final thoughts
There’s a lot to SEO, and strategies may look different depending on the institution and program offerings. Here is an SEO audit summary:
- Focus on using long-tail keywords
- Don’t forget to optimize your videos and images for search engines (you have a higher chance for your images to rank than your content early on!)
- Review the technical health of your website:
- It’s your best online marketing asset – make sure it’s up and running correctly!
- Steer clear of any server-side issues or website code that might be causing delays in pages loading.
- Almost 95% of the time, changing your server settings improves website speed! If your website goes from a 1-second load time to a 5-second load time, the probability of someone bouncing increases by 90%.
- Write great pillar content so you can:
- Easily explain industry terminology
- Rank for more broad keywords
- Land upper funnel audiences on website pages and encourage them to sign up for a newsletter (or another call to action)
- Use this content in your admissions strategy so employees at your institution can easily send relevant information to prospective students
- Pay to promote some of your newly developed high-value content with paid media
Remember, not every piece of content you create will need to rank. Some are designed to help more with conversion, and that’s equally – if not more – important.
In conclusion: Higher Ed SEO helps your university grow enrollment and increase tuition revenue.
For any university, SEO should always have a dedicated seat at your marketing roundtable.
It’s a slow-growth strategy that has a lot of moving parts, but driving more people to your site opens up so many doors for opportunity. Our team is ready to support you if you would like help with your Higher Ed SEO strategy or audit.
Get your free Higher Ed SEO audit!
We help established colleges and universities develop SEO that drives prospects to the next stage in their enrollment journey. Our goal is to help you meet yours. With a long-term SEO strategy in place, you’ll be able to build more authority with your audience while you sleep — and you’ll have more time to focus on what’s next for your institution.

We’ve created several thought leadership articles around content strategy:
- What Is Content Marketing? Why You’re Ignored & How To Fix It
- Content Strategy: 4 Easy Ways to Repurpose Your Content
- 5 Powerful Reasons Why Your Brand Needs to Use Video Marketing
- 5 Reasons Why You Should Blog for Your Business in 2021
- 9 Tips to Create a Strategic Marketing Budget for 2022
- How Your University Can Leverage Admissions Webinars + Replays to Drastically Grow Enrollments
- How to Nurture Your Prospective Students from Inquiry to Enrollment
How to Grow College Enrollments
Quick intermissions to let you know our blog is loaded with articles on how to grow college enrollments:
- Read to learn about how to best market and recruit GenZ and how to win them over
- Brand Storytelling: The Amazing Marketing Tool Everyone Has, But No One Uses
- 6 Secrets To Growing Tuition Revenue Through Smart Enrollment Management
- How to Improve Enrollment in College: Enrollment Strategy + Marketing Tips
- College Marketing Trends to Boost Your Enrollments in 2023
- Higher Ed SEO Audit – Get Your Free SEO Audit Today
- Higher Ed Case Study: Rebranding a College of Business
- How to Run Effective Online Open Houses to Drive Up Enrollments
- How to Repurpose Online Webinar Content into New Video Content
- Targeting Parents In Higher Ed: College Parent Facebook Groups & Other Must-Know Ideas
- Speed-to-Lead: Should Your College be Calling Prospective Students?
- Need a Way to Differentiate Your College? Think Service.
- Best Ways to Use Text Messaging in Your Enrollment Strategy






